The Rise of Cloud Gaming: How It’s Revolutionizing the Gaming Experience
From the rise of online multiplayer to the explosion of mobile gaming, the gaming industry has undergone massive transformations over the last few decades, driven by advancements in technology. However, the advent of cloud gaming — a game-changing technology that could reshape how we play and access video games — has been one of the most significant innovations in recent years.
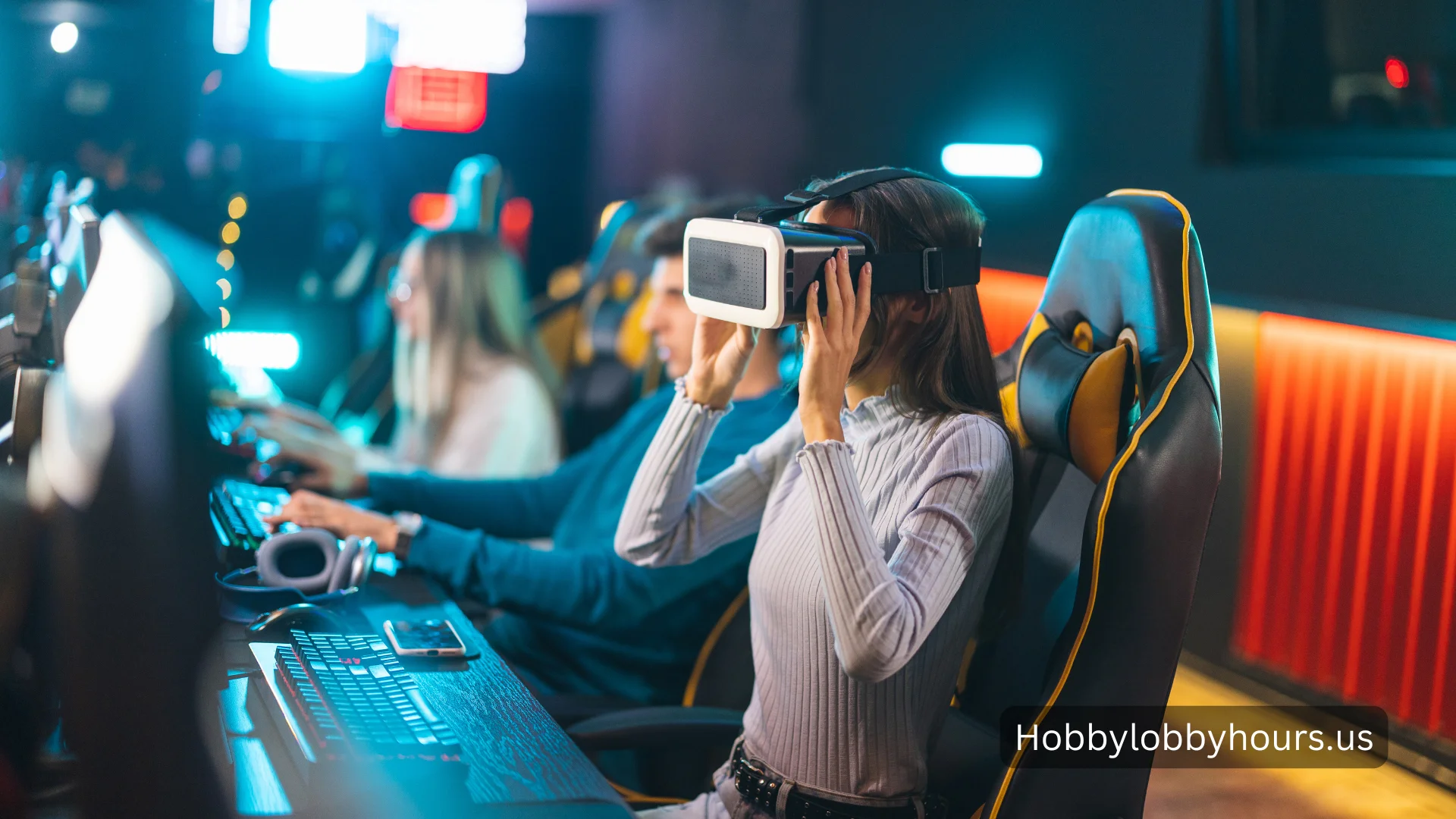
By streaming games to the cloud, players can play games remotely without requiring a powerful local device. A game runs on powerful servers in remote data centers, and players interact with it via an internet connection, rather than running it on a console, PC, or gaming rig. Similar to streaming movies or TV shows on platforms such as Netflix, players stream the game in real time.
We will explore the technology behind cloud gaming, its advantages, challenges, and what the future holds for this rapidly growing industry.

How does cloud gaming work?
In its simplest sense, gaming is the process of streaming video games over the internet from a powerful remote server (often in a data center) to players’ devices. By doing so, the heavy lifting is done remotely, so there is no need for expensive, high-performance hardware.
To play high-end games, players just need a compatible device (smartphone, tablet, PC, laptop, smart TV, etc.) and a reliable internet connection. The game is processed on the server, and only the video and audio are streamed back to the player, along with their input commands (e.g., mouse, keyboard, or controller).
The following are some of the leading gaming services:
- NVIDIA GeForce NOW: You can stream games from popular services like Steam and Epic Games Store to your device using a gaming service.
- Stadia (shutdown in 2023): The Google Stadia service, which offered direct game streaming from Google’s data centers, was one of the first major gaming services to garner attention.
- Xbox Cloud Gaming (xCloud): Streaming Xbox games directly to smartphones, tablets, and PCs is possible through Microsoft’s gaming platform, part of Xbox Game Pass Ultimate.
- PlayStation Plus Premium: A PlayStation 4 or PlayStation 5 game can be streamed using Sony’s gaming service, provided users have a stable internet connection.
Players will be able to access and enjoy their favorite games in a new way thanks to these services.
Cloud gaming technology
In order for gaming to work smoothly, high-performance servers, low-latency internet connections, and cutting-edge software must be combined. Here are the components needed to mak gaming work:
- A powerful server and a data center: Games are played on servers located in large data centers with powerful GPUs and CPUs capable of rendering high-quality graphics on remote servers. These servers can host a variety of games, including those listed on an RSPS list (private RuneScape servers or similar types of custom game servers). To reduce latency and improve streaming quality, data centers are strategically located worldwide to ensure players are connected to the nearest server. Cloud gaming relies on the data center to provide the computational power necessary to run modern games at high resolutions and frame rates.
- Streaming and compression of video: A compressed video and audio file is sent over the internet to the player’s device after the game has been rendered on the server. A high-quality visual experience is maintained while minimizing bandwidth usage through compression techniques. Even with fluctuating internet speeds, advanced codecs like H.265 and VP9 allow high resolution (1080p, 4K) to be maintained.
- Fast Internet with low latency: One of the biggest challenges in gaming is latency — the time it takes for a player’s input to be reflected in the game. A high latency can cause noticeable delays, making fast-paced games unplayable. To ensure minimal delay, gaming companies use low-latency protocols and content delivery networks (CDNs). In order to avoid lag and buffering, you need a high-speed internet connection (typically 15-30 Mbps for 1080p gaming).
- Processing user input: Traditionally, inputs from the controller or keyboard were processed locally on the device. In gaming, these inputs were sent to the remote server, which then processed them and sent the updated game state back to the player. It is imperative that this round-trip process is as fast as possible to prevent a delay in the response of the game to the player’s actions.
Also check: What Makes Game Art and Game Design Different
Cloud gaming’s advantages
There are several key advantages to gaming that could redefine the future of gaming:
- Hardware is not required: There are many obvious benefits to playing AAA games on a basic device, such as a smartphone, tablet, or even an older PC, instead of investing in expensive gaming PCs and consoles. As a result, high-end gaming becomes more affordable for a broader audience and is democratized. The affordable price of gaming serves as an anchor for its growth, enabling high-performance games to be accessible to gamers who might otherwise not be able to afford them.
- Games are available instantly: A gaming service often offers a wide selection of games that can be played instantly. Players do not have to install or download anything. They can simply stream the game and get started immediately.
- Play across platforms: Modern gamers benefit from cross-platform play on many gaming platforms, which allows them to start a game on one device (e.g., PC) and continue it on another (e.g., smartphone or tablet).
- Expansion of the game library and preservation of games: The cloud can offer access to a wide pool of games, including those that may not be supported on current hardware. This preserves classic titles and opens up new content options.
- Instant updates and scalability: A cloud-based platform can be quickly updated and scaled, which ensures that all players have access to the latest games, patches, and features.
Cloud gaming challenges
In spite of cloud gaming’s promising potential, it faces a number of significant challenges:
- Limitations on latency and bandwidth: Even with the latest technological advances, latency remains a key issue, especially for fast-paced genres like first-person shooters (FPS) or competitive multiplayer games. Those living in remote areas or with slower internet speeds may encounter lag, making the experience less enjoyable.
- Connectivity to the Internet is dependent on: There is a need for a stable and fast internet connection for gaming. This could limit gaming availability in areas where the internet infrastructure is poor or the cost of data is high. Internet outages and fluctuations in speed can also disrupt gameplay. Cloud gaming’s accessibility and overall performance are heavily dependent on the quality of the player’s internet service.
- Ownership and control of the game:
- It is often the case that players do not truly own the games they play when they use gaming services, as they are typically subscribed to or rented. A service closing can result in players losing access to their entire library of games. A major drawback for some is the loss of ownership. A key issue in this case is the business model of gaming services, which may not be aligned with players’ expectations of game ownership and permanence.
- Concerns regarding storage and data:
- Streaming games can consume a lot of data, especially for high-resolution games. In regions where internet providers limit bandwidth usage, players may experience throttled speeds or additional charges if they run into data caps.
Gaming in the Cloud: The Future
The future of gaming is bright despite these challenges. Advances in 5G networks, low-latency internet technologies, and AI-driven compression techniques are poised to propel the industry forward. Cloud gaming may also offer more immersive experiences when integrated with platforms like Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR).
There is a possibility that gaming platforms will become more sophisticated as competition intensifies, offering enhanced game libraries, better streaming quality, and more robust cross-platform compatibility. As a delivery platform, gaming may also gain popularity among traditional game developers, further driving its adoption.
Conclusion
As the technology advances rapidly, cloud gaming may soon become the standard for video games everywhere. While there are still hurdles to overcome, cloud gaming is set to revolutionize the way we play and access video games. A cloud-anchored, high-quality gaming experience will be available anywhere, anytime, on any device.